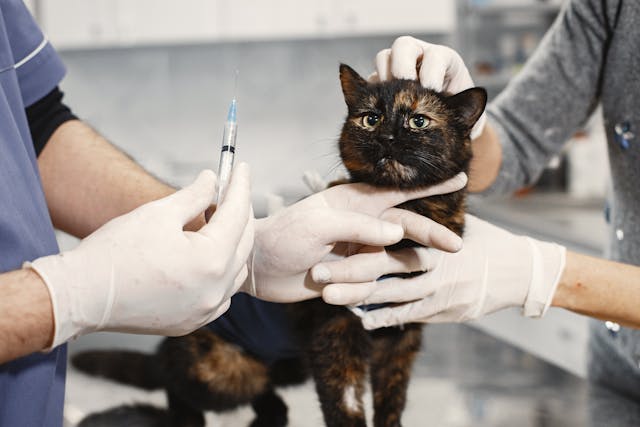
 Vaccinations are vital because they help prevent your pet from contracting contagious diseases that could severely impact their health. Much like human vaccines, pet vaccines stimulate the immune system to recognize and fight off specific pathogens, creating immunity. Vaccines are a simple yet effective way to avoid costly treatments and long-term health problems that could arise from infectious diseases.
Vaccinations are vital because they help prevent your pet from contracting contagious diseases that could severely impact their health. Much like human vaccines, pet vaccines stimulate the immune system to recognize and fight off specific pathogens, creating immunity. Vaccines are a simple yet effective way to avoid costly treatments and long-term health problems that could arise from infectious diseases.
Core vs. Non-Core Vaccines
Vaccines are typically divided into two categories: core and non-core vaccines.
Core Vaccines:
These are vaccines that are recommended for all pets, as they protect against the most common and severe diseases. Core vaccines include:
- Rabies: A fatal virus affecting the nervous system. Rabies is a public health concern, as it can be transmitted to humans.
- Distemper: A viral disease that affects the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and nervous systems.
- Parvovirus: A highly contagious viral infection that affects the intestines, causing severe vomiting and diarrhea.
- Adenovirus (Canine Hepatitis): This vaccine protects against a virus that attacks the liver and can lead to severe illness or death.
Non-Core Vaccines:
These are optional vaccines based on your pet’s lifestyle, environment, and risk factors. They include:
- Bordetella (Kennel Cough): Recommended for pets that are in contact with other animals in places like boarding facilities, dog parks, or grooming centers.
- Leptospirosis: Important for pets in areas with standing water, as the bacteria that causes leptospirosis can be found in wet environments. Highly recommended for pets in Pensacola.
- Lyme Disease: Recommended if your pet lives in areas where ticks are prevalent. Not a usual vaccine for Pensacola but may be recommended depending on your pets lifestyle. I.e. hunting dog or pets that travel to areas that have Lyme Disease.
Pet Vaccination Schedule for Dogs at Coastal Sunrise Animal Hospital
Puppies (6-16 Weeks)
Puppies have developing immune systems and need a series of vaccinations to help protect them in the first few months of life. The schedule typically includes:
6-8 weeks:
- Distemper, Parvovirus, Adenovirus, Parainfluenza (DA2PP): First combination vaccine.
9-11 weeks:
- DA2PP: Second dose.
- Bordetella
12-15 weeks:
- DA2PP: Final dose.
- Leptospirosis: first dose, ..
16 weeks:
- DA2PP: Final dose.
- Leptospirosis: Second dose
- Rabies
After the initial puppy series, booster shots are required every 1 to 3 years, depending on the vaccine.
Adult Dogs (1 Year and Older)
Once your dog reaches adulthood, their vaccination schedule shifts. Annual or triennial boosters
(depending on the vaccine) are recommended. Your dog will need:
- Rabies: Required by law in many areas, usually every 1 to 3 years.
- DA2PP: Boosters every 1 to 3 years, depending on the vaccine used.
- Leptospirosis, Lyme, Bordetella: Depending on lifestyle and exposure, we may recommend annual or triennial boosters.
Pet Vaccination Schedule for Cats
Kittens (6-16 Weeks)
Like puppies, kittens need a series of vaccinations to protect them from diseases early in life.
6-8 weeks:
- Feline Distemper (FVRCP): Combination vaccine protecting against feline viral rhinotracheitis, calicivirus, and panleukopenia.
9-11 weeks:
- FVRCP: Second dose.
- Leukemia (FeLV): First dose, if required.
12-15 weeks:
- FVRCP: 3rd dose
- Leukemia (FeLV): 2nd dose,
16 weeks:
- FVRCP: 4th dose
- Rabies
After this kitten series, annual or triennial boosters will be required.
Adult Cats (1 Year and Older)
Once your cat reaches adulthood, they’ll need a maintenance schedule that includes:
- Rabies: Required every 1-3 years, depending on local regulations.
- FVRCP: Boosters every 1-3 years.
- FeLV: Annual vaccination, if your cat is at risk of exposure.
Important Considerations
- Regular Checkups: Vaccinations are often given during routine checkups, but regular health visits also ensure that your pet is in good condition overall.
- Keep Records: Maintain a vaccination record to ensure that your pet gets timely boosters and stays up-to-date on their shots.
- Travel and Boarding: If you’re traveling with your pet or boarding them, ensure that vaccinations like Bordetella or others required by the facility are up-to-date.
Conclusion
Vaccinations are a critical component of your pet’s health care plan. By following the recommended vaccination schedule you can help ensure that your pet lives a long, happy, and healthy life. Protect your furry friend by staying on top of their vaccinations, and always be proactive in seeking expert advice for their well-being.
